接上文 理解 Linux 中的 splice(2),本篇来探讨一下 splice 的几个参数配置
SPLICE_F_MORE#
splice 系统调用的 flag 参数可以为一下几个的组合
SPLICE_F_MOVE:一个实际上没有被使用的参数SPLICE_F_NONBLOCK:非阻塞,需要传入的文件描述符也为非阻塞模式才能生效SPLICE_F_MORE:提示在后续的splice操作中会传输更多的数据,在fd_out是 socket 的时候会有帮助SPLICE_F_GIFT:splice中没有用到的参数
除了 SPLICE_F_MORE 外,其他的应该不难理解。接下来说一下这个参数的意义。实验环境延续上文,使用 splice 来构筑一个 TCP Proxy,通过 curl 命令来下载 Server 端的大小为 100MB 的文件,中间 Proxy 会使用 splice 来将 Client 的 data 写入 pipe,然后再从 pipe 中读取 data 转发到 Server 中;反向过程的数据也是一样处理的
首先我们在写入 socket 的时候设置一个这个 SPLICE_F_MORE 来做一下 benchmark。测试的系统配置如下, MTU 65536
$ cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_rmem
4096 131072 6291456
$ cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_wmem
4096 16384 4194304
const PAGE_SIZE: usize = 4096; // 机器的 PAGE_SIZE 大小
const PIPE_SIZE: usize = PAGE_SIZE * 16; // pipe 的 buffer size
const READ_SIZE: usize = PAGE_SIZE * 16; // 从 socket 到 pipe 时 splice 的 len 参数
const WRITE_SIZE: usize = PAGE_SIZE * 16; // 从 pipe 到 socket 时 splice 的 len 参数
不设置 SPLICE_F_MORE :(测试工具为 k6,参数为 30s,1 VU,每次请求不复用 TCP 连接)
data_received..................: 41 GB 1.4 GB/s
data_sent......................: 44 kB 1.5 kB/s
设置 SPLICE_F_MORE 后:
data_received..................: 11 GB 367 MB/s
data_sent......................: 12 kB 389 B/s
可以看到传输性能明显下降了大约 4 倍。那么为什么呢?我们来看一下代码,调用路径和上一篇文章中提到的类似,这里只摘录一下关键的部位
// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.3/fs/splice.c#L1114
/*
* Determine where to splice to/from.
*/
long do_splice(struct file *in, loff_t *off_in, struct file *out,
loff_t *off_out, size_t len, unsigned int flags)
// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.3/fs/splice.c#L851
/*
* Attempt to initiate a splice from pipe to file.
*/
static long do_splice_from(struct pipe_inode_info *pipe, struct file *out,
loff_t *ppos, size_t len, unsigned int flags)
// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.3/fs/splice.c#L832
/**
* generic_splice_sendpage - splice data from a pipe to a socket
* @pipe: pipe to splice from
* @out: socket to write to
* @ppos: position in @out
* @len: number of bytes to splice
* @flags: splice modifier flags
*
* Description:
* Will send @len bytes from the pipe to a network socket. No data copying
* is involved.
*
*/
ssize_t generic_splice_sendpage(struct pipe_inode_info *pipe, struct file *out,
loff_t *ppos, size_t len, unsigned int flags)
{
return splice_from_pipe(pipe, out, ppos, len, flags, pipe_to_sendpage);
}
pipe_to_sendpage 是处理数据用的 handler,会将 pipe 的数据写入 socket 中
// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.3/fs/splice.c#L438
/*
* Send 'sd->len' bytes to socket from 'sd->file' at position 'sd->pos'
* using sendpage(). Return the number of bytes sent.
*/
static int pipe_to_sendpage(struct pipe_inode_info *pipe,
struct pipe_buffer *buf, struct splice_desc *sd)
{
struct file *file = sd->u.file;
loff_t pos = sd->pos;
int more;
if (!likely(file->f_op->sendpage))
return -EINVAL;
more = (sd->flags & SPLICE_F_MORE) ? MSG_MORE : 0;
if (sd->len < sd->total_len &&
pipe_occupancy(pipe->head, pipe->tail) > 1)
more |= MSG_SENDPAGE_NOTLAST;
return file->f_op->sendpage(file, buf->page, buf->offset,
sd->len, &pos, more);
}
通过这个函数我们可以看到,如果设置了 SPLICE_F_MORE 那么会追加 MSG_MORE flag;如果当前 pipe 中还有其他的 page,则追加 MSG_SENDPAGE_NOTLAST flag。
首先来看 MSG_MORE 的作用,熟悉 TCP 的应该已经知道了这个标志表示调用者有更多的数据要发送。在 TCP socket 中,该标志用于获取与 TCP_CORK 相同的效果,不同之处在于该标志可以在每次调用时设置。顾名思义 TCP_CORK 就是给 TCP 发送数据的时候加了一个木塞子。往这个 socket 写入的数据都会聚集起来。虽然堵上了塞子,但是数据总得发送,取决于:
- 程序取消设置 TCP_CORK 这个选项
- socket 聚集的数据大于一个 MSS 的大小
- 自从堵上塞子写入第一个字节开始,已经经过 200ms
- socket 被关闭了
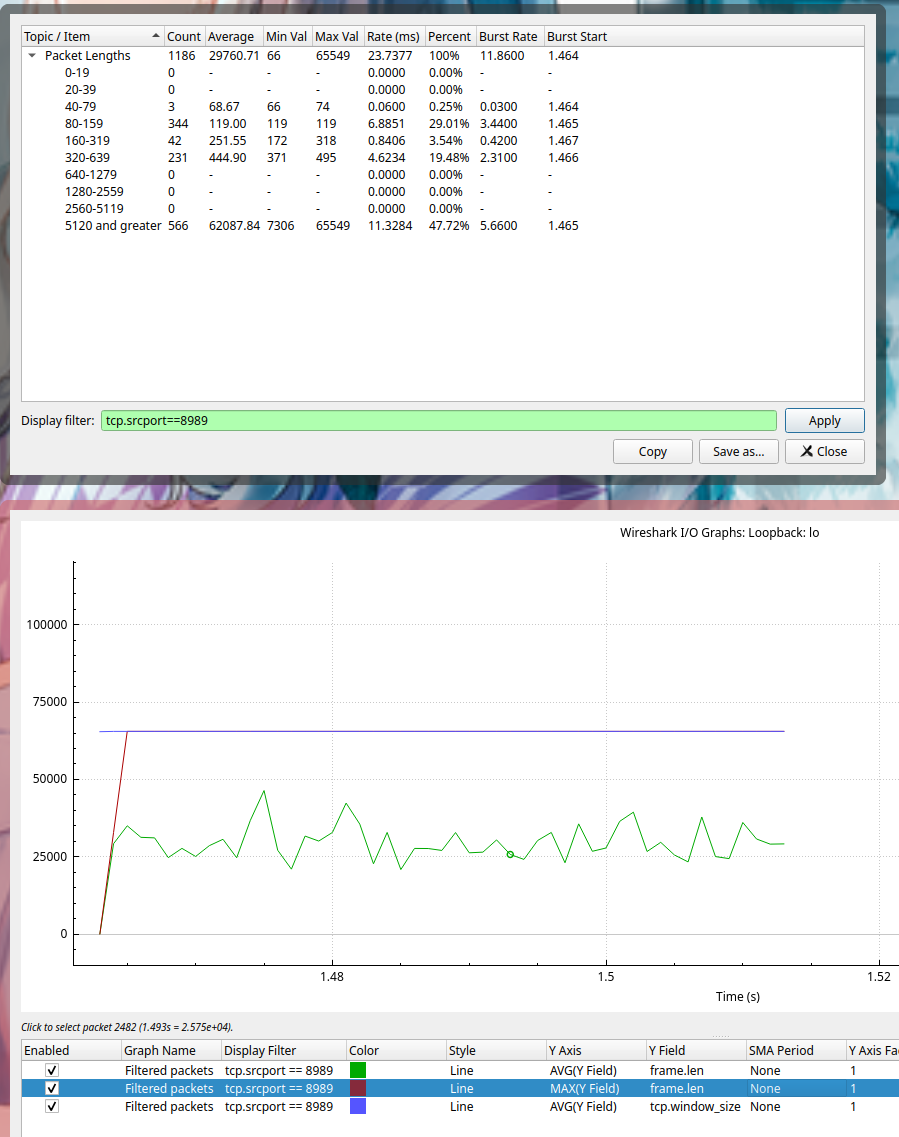
接下来我们通过流量分析来看一下数据,工具使用的是 wireshark,抓取的 client 到 proxy 的数据。proxy 的端口是 8989,下图都已经过滤好了,只显示了 8989 到 client 的流量,也就是那 100 MB 的文件
在不设置 SPLICE_F_MORE 的情况下
设置 SPLICE_F_MORE 的情况下
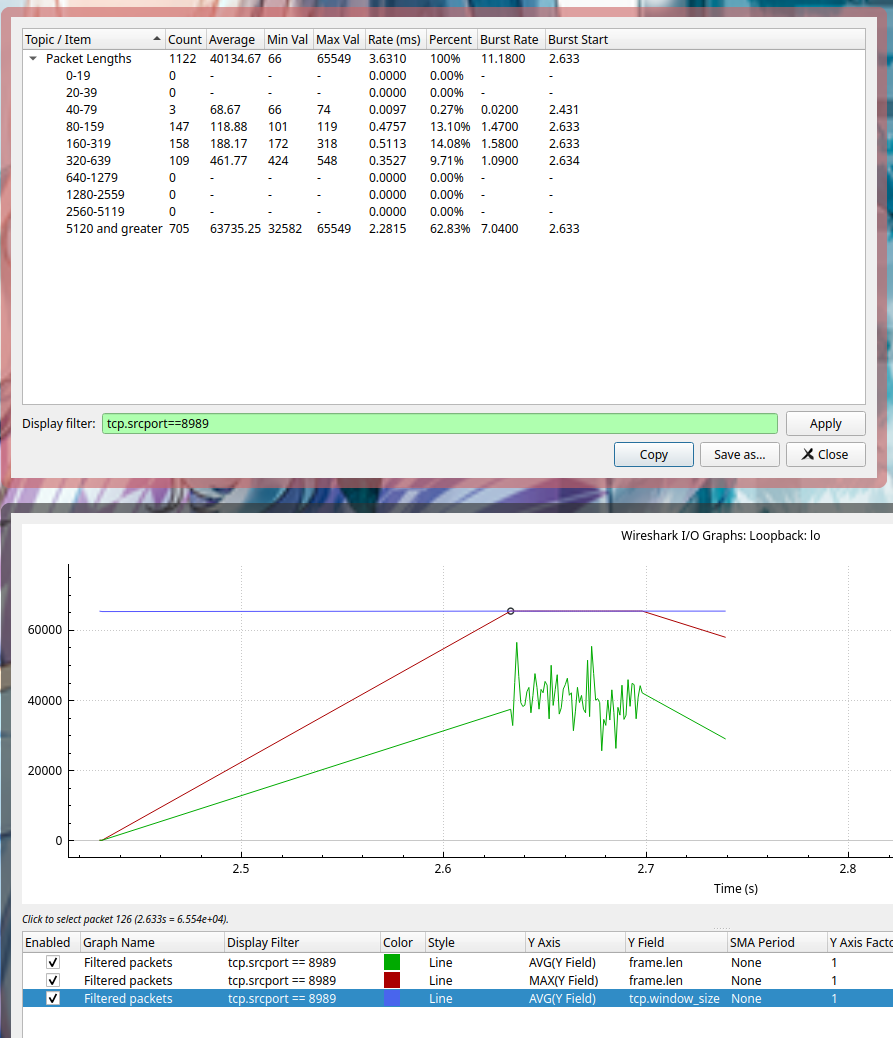
可能会有人觉得上图为什么有一条固定斜率的斜线,其实这个地方是没有流量的,只是 wireshark 在画图的时候会将散点连接起来。横轴一小格表示 20 ms,这个时间区间大概是 2.43 到 2.64 左右,正好有相当于 200ms 的空白。所以在每次请求的时候我们都浪费了 200 ms 的时间,等待数据的大小到达 MTU 65535。但是由于 TCP 本身的慢启动机制,导致每次都很难快速填满,从而会造成一个停等的状态
综上所述,使用 SPLICE_F_MORE 的时候需要考虑数据的上下行传输速率还有自身配置的 MTU 大小,配置不当会起反作用
SPLICE_F_NONBLOCK#
这个参数一般不会用错,但是这里还是提一下把。从一个问题入手,如果我的 pipe 没有设置 O_NONBLOCK flag,然后我在 splice 的时候传入的参数有 SPLICE_F_NONBLOCK 的,那么这个会阻塞么?我们直接来看代码
// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.3/fs/splice.c#L1094
long splice_file_to_pipe(struct file *in,
struct pipe_inode_info *opipe,
loff_t *offset,
size_t len, unsigned int flags)
{
long ret;
pipe_lock(opipe);
ret = wait_for_space(opipe, flags);
if (!ret)
ret = do_splice_to(in, offset, opipe, len, flags);
pipe_unlock(opipe);
if (ret > 0)
wakeup_pipe_readers(opipe);
return ret;
}
主要看一下 wait_for_space 的实现
// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.3/fs/splice.c#L1073
static int wait_for_space(struct pipe_inode_info *pipe, unsigned flags)
{
for (;;) {
if (unlikely(!pipe->readers)) {
send_sig(SIGPIPE, current, 0);
return -EPIPE;
}
if (!pipe_full(pipe->head, pipe->tail, pipe->max_usage))
return 0;
if (flags & SPLICE_F_NONBLOCK)
return -EAGAIN;
if (signal_pending(current))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
pipe_wait_writable(pipe);
}
}
在循环里面,如果 pipe_full 条件为真,那么接下来判断的是此次调用是否有 SPLICE_F_NONBLOCK flag,根本没有理会 pipe 自己的 flag。所以其实不需要 pipe 去设置 O_NONBLOCK 只需要在每次调用 splice 的时候写对就可以了
关于 Pipe buf size#
第三个问题我们来研究一下 Pipe 的 buffer size,下面会简称为 BUF_SIZE。此值的上限定义在 /proc/sys/fs/pipe-max-size 中
>> cat /proc/sys/fs/pipe-max-size
1048576
这个值正好是 256 个 PAGE_SIZE 的大小
>> getconf PAGESIZE
4096
为什么呢,其实结合上一篇文章涉及的一些代码片段就可以理解。Pipe 其实管理的是 Page 的数组,正确理解应该是一个环形数组。既然管理的单位是 Page,那么我们有可能将大小设置为 2048 (4096 /2) 么,或者设置为 12288(4096 * 3) 么。我们带着问题来看一下
fcntl 函数在通过 F_SETPIPE_SZ 设置 BUF_SIZE 成功后会返回当前的大小,做一下实验
PIPE_SIZE = 2048 => return 4096
PIPE_SIZE = 4096 => return 4096
PIPE_SIZE = 8192 => return 8192
PIPE_SIZE = 12288 => return 16384
PIPE_SIZE = 16384 => return 16384
PIPE_SIZE = 20480 => return 32768
很显然这个参数并不是随便设置的,而且也不是 PAGE_SIZE 的整数倍,必须要 PAGE_SIZE 的 2^n 倍才行,如果不足那么向上靠拢。这个算法是不是很眼熟,在 hashmap 扩容的时候经常用到。此部分的实现可以参考
// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.3/fs/pipe.c#L1385
// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.3/fs/pipe.c#L1317
/*
* Allocate a new array of pipe buffers and copy the info over. Returns the
* pipe size if successful, or return -ERROR on error.
*/
static long pipe_set_size(struct pipe_inode_info *pipe, unsigned long arg)
{
unsigned long user_bufs;
unsigned int nr_slots, size;
long ret = 0;
size = round_pipe_size(arg);
nr_slots = size >> PAGE_SHIFT;
/*
* If trying to increase the pipe capacity, check that an
* unprivileged user is not trying to exceed various limits
* (soft limit check here, hard limit check just below).
* Decreasing the pipe capacity is always permitted, even
* if the user is currently over a limit.
*/
if (nr_slots > pipe->max_usage &&
size > pipe_max_size && !capable(CAP_SYS_RESOURCE))
return -EPERM;
user_bufs = account_pipe_buffers(pipe->user, pipe->nr_accounted, nr_slots);
if (nr_slots > pipe->max_usage &&
(too_many_pipe_buffers_hard(user_bufs) ||
too_many_pipe_buffers_soft(user_bufs)) &&
pipe_is_unprivileged_user()) {
ret = -EPERM;
goto out_revert_acct;
}
ret = pipe_resize_ring(pipe, nr_slots);
if (ret < 0)
goto out_revert_acct;
pipe->max_usage = nr_slots;
pipe->nr_accounted = nr_slots;
return pipe->max_usage * PAGE_SIZE;
out_revert_acct:
(void) account_pipe_buffers(pipe->user, nr_slots, pipe->nr_accounted);
return ret;
}
在这里我们可以看到还有条件被参与计算 too_many_pipe_buffers_hard 和 too_many_pipe_buffers_soft。此参数可以通过下面两个文件进行配置
>> cat /proc/sys/fs/pipe-user-pages-hard
0
>> cat /proc/sys/fs/pipe-user-pages-soft
16384
splice 的 len 参数和 pipe buf size 的关系#
最后一个问题,在上一篇文章中,我们看到在从 socket buffer 到 pipe 做数据映射的时候,定义了 splice_pipe_desc 类型的结构体 spd,其中 pages 指针数组的大小是 MAX_SKB_FRAGS。
// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.3/net/core/skbuff.c#L2921
/*
* Map data from the skb to a pipe. Should handle both the linear part,
* the fragments, and the frag list.
*/
int skb_splice_bits(struct sk_buff *skb, struct sock *sk, unsigned int offset,
struct pipe_inode_info *pipe, unsigned int tlen,
unsigned int flags)
{
struct partial_page partial[MAX_SKB_FRAGS];
struct page *pages[MAX_SKB_FRAGS];
struct splice_pipe_desc spd = {
.pages = pages,
.partial = partial,
.nr_pages_max = MAX_SKB_FRAGS,
.ops = &nosteal_pipe_buf_ops,
.spd_release = sock_spd_release,
};
int ret = 0;
__skb_splice_bits(skb, pipe, &offset, &tlen, &spd, sk);
if (spd.nr_pages)
ret = splice_to_pipe(pipe, &spd);
return ret;
}
然后在复制 page 地址的时候,这里有两个条件会结束循环
pipe_full(head, tail, pipe->max_usage)spd->nr_pages == 0
// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.3/fs/splice.c#L182
/**
* splice_to_pipe - fill passed data into a pipe
* @pipe: pipe to fill
* @spd: data to fill
*
* Description:
* @spd contains a map of pages and len/offset tuples, along with
* the struct pipe_buf_operations associated with these pages. This
* function will link that data to the pipe.
*
*/
ssize_t splice_to_pipe(struct pipe_inode_info *pipe,
struct splice_pipe_desc *spd)
{
unsigned int spd_pages = spd->nr_pages;
unsigned int tail = pipe->tail;
unsigned int head = pipe->head;
unsigned int mask = pipe->ring_size - 1;
int ret = 0, page_nr = 0;
while (!pipe_full(head, tail, pipe->max_usage)) {
struct pipe_buffer *buf = &pipe->bufs[head & mask];
buf->page = spd->pages[page_nr];
buf->offset = spd->partial[page_nr].offset;
buf->len = spd->partial[page_nr].len;
buf->private = spd->partial[page_nr].private;
buf->ops = spd->ops;
buf->flags = 0;
head++;
pipe->head = head;
page_nr++;
ret += buf->len;
if (!--spd->nr_pages)
break;
}
if (!ret)
ret = -EAGAIN;
return ret;
}
nr_pages 的值是不会超过 MAX_SKB_FRAGS 的。在我的系统中,这个大小是
>> sysctl net.core.max_skb_frags
net.core.max_skb_frags = 17
那么是否意味着即使我们对 Pipe 的 buf size 设置的非常大,但是我们每次调用 splice 的时候都无法超过 69632(17 * 4096) 呢?我们可以做一下实验
const PAGE_SIZE: usize = 4096;
const PIPE_SIZE: usize = PAGE_SIZE * 32;
const READ_SIZE: usize = PAGE_SIZE * 32;
const WRITE_SIZE: usize = PAGE_SIZE * 32;
通过 strace 来截获系统调用,可以发现这个返回的值是可以大于 69632 的
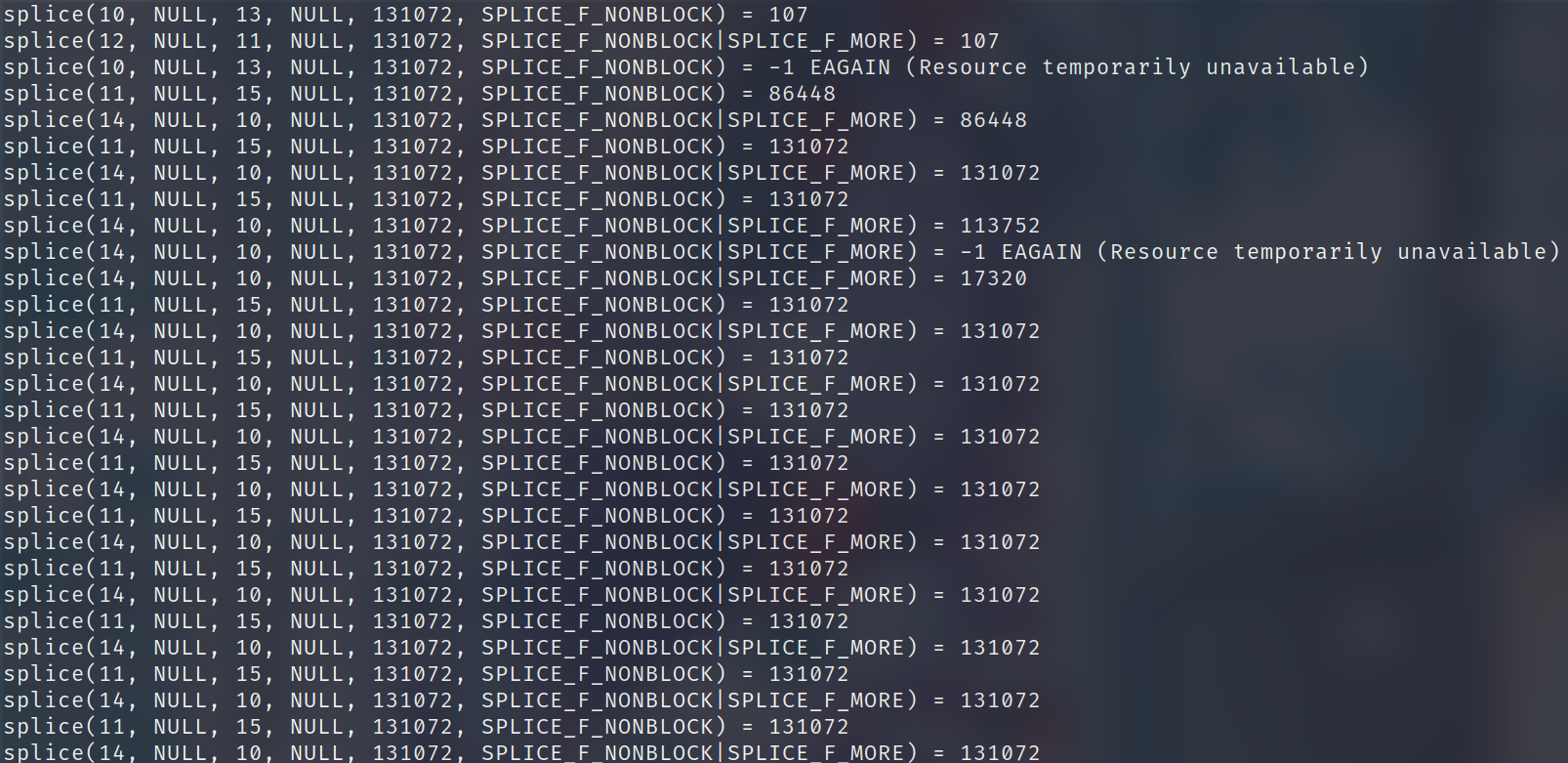
为什么呢?因为在 splice 的最开始的地方 tcp_splice_read 这里使用了一个循环来判断是否达到我们传入的 len 参数的大小。当 kernel 中一轮 splice_to_pipe 结束后,如果没有达到我们要求的大小,且 pipe 还有剩余的空间。那么这里是会重复上述流程的。而且这里在每一轮结束后都会释放 socket 的锁,使得 ksoftirqd 有机会来传送数据到 socket buffer
// https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/v6.3/net/ipv4/tcp.c#L769
/**
* tcp_splice_read - splice data from TCP socket to a pipe
* @sock: socket to splice from
* @ppos: position (not valid)
* @pipe: pipe to splice to
* @len: number of bytes to splice
* @flags: splice modifier flags
*
* Description:
* Will read pages from given socket and fill them into a pipe.
*
**/
ssize_t tcp_splice_read(struct socket *sock, loff_t *ppos,
struct pipe_inode_info *pipe, size_t len,
unsigned int flags)
{
struct sock *sk = sock->sk;
struct tcp_splice_state tss = {
.pipe = pipe,
.len = len,
.flags = flags,
};
// ...
lock_sock(sk);
while (tss.len) {
ret = __tcp_splice_read(sk, &tss);
// ...
tss.len -= ret;
release_sock(sk);
lock_sock(sk);
}
release_sock(sk);
return ret;
}
Reference#
推荐阅读下面这篇文章