本文基于Kubernetes v1.21.2, commit sha 为 092fbfbf53427de67cac1e9fa54aaa09a28371d7
承接上文,我们来继续看 syncLoop 中的内容
pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go:1845
// syncLoop is the main loop for processing changes. It watches for changes from
// three channels (file, apiserver, and http) and creates a union of them. For
// any new change seen, will run a sync against desired state and running state. If
// no changes are seen to the configuration, will synchronize the last known desired
// state every sync-frequency seconds. Never returns.
func (kl *Kubelet) syncLoop(updates <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate, handler SyncHandler) {
plegCh := kl.pleg.Watch()
// Responsible for checking limits in resolv.conf
// The limits do not have anything to do with individual pods
// Since this is called in syncLoop, we don't need to call it anywhere else
if kl.dnsConfigurer != nil && kl.dnsConfigurer.ResolverConfig != "" {
// 1. 打开 /etc/resolves.conf 并解析
kl.dnsConfigurer.CheckLimitsForResolvConf()
}
for {
// 2. .. 省略: 如果自身状态异常,那么会进行一个初始值为 100 毫秒,上限为 5 秒的二进制指数退避 sleep
// 3. 执行主要逻辑,从不同的 channel 中接收消息并分发处理
// syncTicker 是 duration 为 1 秒的 Ticker; housekeepingTicker 则是 2 秒
if !kl.syncLoopIteration(updates, handler, syncTicker.C, housekeepingTicker.C, plegCh) {
break
}
}
}
这里对于 DNS 的配置文件进行检查,CheckLimitsForResolvConf 做了以下的事情
- 打开 /etc/resolv.conf, 并解析。如果出错则打印日志并产生一条 Event
- 如果 search path 上的 domain 的大于 MaxDNSSearchPaths 则打印日志并产生一条 Event。MaxDNSSearchPaths 的值为 6
- 如果 search path 的长度超过 MaxDNSSearchListChars 则打印日志病产生一条 Event, MaxDNSSearchListChars 的值为 256
/etc/resolv.conf 的内容如下:
$ cat /etc/resolv.conf
search lan
nameserver 192.168.199.1
对于 seach 项进行检查是因为 Linux 的低版本的 glibc 限制,参考 https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man5/resolv.conf.5.html
In glibc 2.25 and earlier, the search list is limited to six domains with a total of 256 characters. Since glibc 2.26, the search list is unlimited.
kubelet 的核心逻辑位于 pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go:1919 的 syncLoopIteration 函数中,不过本篇我们先略过这个,来看看 kubelet 的 PodWorker
func (kl *Kubelet) syncLoopIteration(
configCh <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate,
handler SyncHandler,
syncCh <-chan time.Time,
housekeepingCh <-chan time.Time,
plegCh <-chan *pleg.PodLifecycleEvent
) bool {
select {
case u, open := <-configCh:
// Update from a config source; dispatch it to the right handler
// callback.
if !open {
klog.ErrorS(nil, "Update channel is closed, exiting the sync loop")
return false
}
switch u.Op {
case kubetypes.ADD:
klog.V(2).InfoS("SyncLoop ADD", "source", u.Source, "pods", format.Pods(u.Pods))
// After restarting, kubelet will get all existing pods through
// ADD as if they are new pods. These pods will then go through the
// admission process and *may* be rejected. This can be resolved
// once we have checkpointing.
handler.HandlePodAdditions(u.Pods)
// .. 省略其他事件类型
default:
klog.ErrorS(nil, "Invalid operation type received", "operation", u.Op)
}
// .. 省略: 部分 channel 的消息处理
}
return true
}
所有的 handler.HandlePodXXX 的函数最终都会调用 dispatchWork 这个函数进行任务的分发处理
pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go:2032
func (kl *Kubelet) dispatchWork(pod *v1.Pod, syncType kubetypes.SyncPodType, mirrorPod *v1.Pod, start time.Time) {
// check whether we are ready to delete the pod from the API server (all status up to date)
containersTerminal, podWorkerTerminal := kl.podAndContainersAreTerminal(pod)
if pod.DeletionTimestamp != nil && containersTerminal {
klog.V(4).InfoS("Pod has completed execution and should be deleted from the API server", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "syncType", syncType)
kl.statusManager.TerminatePod(pod)
return
}
// optimization: avoid invoking the pod worker if no further changes are possible to the pod definition
// (i.e. the pod has completed and its containers have been terminated)
if podWorkerTerminal && containersTerminal {
klog.V(4).InfoS("Pod has completed and its containers have been terminated, ignoring remaining sync work", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "syncType", syncType)
return
}
// Run the sync in an async worker.
kl.podWorkers.UpdatePod(&UpdatePodOptions{
Pod: pod,
MirrorPod: mirrorPod,
UpdateType: syncType,
OnCompleteFunc: func(err error) {
if err != nil {
metrics.PodWorkerDuration.WithLabelValues(syncType.String()).Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(start))
}
},
})
// Note the number of containers for new pods.
if syncType == kubetypes.SyncPodCreate {
metrics.ContainersPerPodCount.Observe(float64(len(pod.Spec.Containers)))
}
}
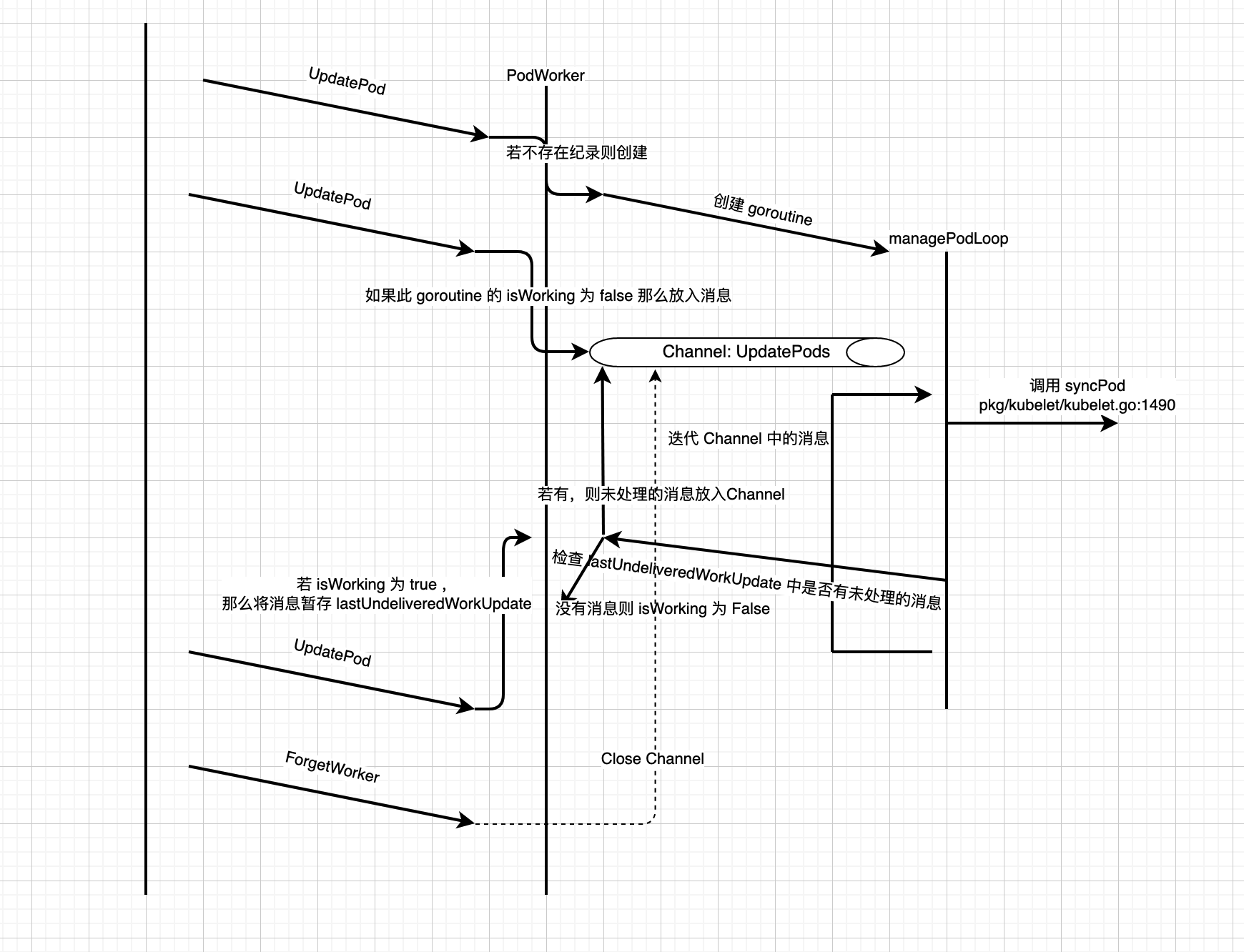
这里便会调用到 PodWorker 中的 UpdatePod 函数。PodWorker 实现了一个 goroutine 池来管理 Pod
Per Pod Goroutine 的创建#
pkg/kubelet/pod_workers.go:199
// Apply the new setting to the specified pod.
// If the options provide an OnCompleteFunc, the function is invoked if the update is accepted.
// Update requests are ignored if a kill pod request is pending.
func (p *podWorkers) UpdatePod(options *UpdatePodOptions) {
pod := options.Pod
uid := pod.UID
var podUpdates chan UpdatePodOptions
var exists bool
p.podLock.Lock()
defer p.podLock.Unlock()
if podUpdates, exists = p.podUpdates[uid]; !exists {
// We need to have a buffer here, because checkForUpdates() method that
// puts an update into channel is called from the same goroutine where
// the channel is consumed. However, it is guaranteed that in such case
// the channel is empty, so buffer of size 1 is enough.
podUpdates = make(chan UpdatePodOptions, 1)
p.podUpdates[uid] = podUpdates
// Creating a new pod worker either means this is a new pod, or that the
// kubelet just restarted. In either case the kubelet is willing to believe
// the status of the pod for the first pod worker sync. See corresponding
// comment in syncPod.
go func() {
defer runtime.HandleCrash()
p.managePodLoop(podUpdates)
}()
}
if !p.isWorking[pod.UID] {
p.isWorking[pod.UID] = true
podUpdates <- *options
} else {
// if a request to kill a pod is pending, we do not let anything overwrite that request.
update, found := p.lastUndeliveredWorkUpdate[pod.UID]
if !found || update.UpdateType != kubetypes.SyncPodKill {
p.lastUndeliveredWorkUpdate[pod.UID] = *options
}
}
}
对于每一个 Pod,都会有一个 goroutine 负责管理,它所执行的函数是 managePodLoop。podWorkers 的工作就是管理这些 goroutine 。对于一个新的 Pod,PodWorker 首先会创建一个 channel podUpdates,然后赋值到自己的 map p.podUpdates 中,这个 map 维护了所有 goroutine 的消息输入端, close 这个 channel 便可以使对应的 goroutine 退出。UpdatePod 函数会被频繁调用,消息只有在 Pod 的 管理 goroutine 的 isWorking 条件为 false 的时候才会被直接传入 channel,否则会放到 lastUndeliveredWorkUpdate 中。这个变量维护了最近一个没有被处理的消息。SyncPodKill 类型的消息具有最高的优先级,如果当 lastUndeliveredWorkUpdate 中的消息为 SyncPodKill 时,之后任何的消息都不能覆盖掉它。为什么这里需要 lastUndeliveredWorkUpdate 而不是消息都直接放入 channel 呢?因为 Kubernetes 是按照最终状态对齐的,比如我们这里连续的 3 个 SyncPodUpdate 消息过来,managePodLoop 是按照最新的 Spec 去更新的,所以会产生两次的重复更新。lastUndeliveredWorkUpdate 的作用便是缓冲并合并
Per Pod Goroutine 的销毁#
当触发 HandlePodRemoves 操作的时候会删除对应 Pod 的管理 goroutine,对应的调用栈为
pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go:2130 HandlePodRemoves
pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go:1761 deletePod
pkg/kubelet/pod_workers.go:246 removeWorder
func (p *podWorkers) removeWorker(uid types.UID) {
if ch, ok := p.podUpdates[uid]; ok {
close(ch)
delete(p.podUpdates, uid)
// If there is an undelivered work update for this pod we need to remove it
// since per-pod goroutine won't be able to put it to the already closed
// channel when it finishes processing the current work update.
delete(p.lastUndeliveredWorkUpdate, uid)
}
}
func (p *podWorkers) ForgetWorker(uid types.UID) {
p.podLock.Lock()
defer p.podLock.Unlock()
p.removeWorker(uid)
}
Per Pod Goroutine 的工作#
pkg/kubelet/pod_workers.go:157
func (p *podWorkers) managePodLoop(podUpdates <-chan UpdatePodOptions) {
var lastSyncTime time.Time
for update := range podUpdates {
err := func() error {
podUID := update.Pod.UID
// This is a blocking call that would return only if the cache
// has an entry for the pod that is newer than minRuntimeCache
// Time. This ensures the worker doesn't start syncing until
// after the cache is at least newer than the finished time of
// the previous sync.
status, err := p.podCache.GetNewerThan(podUID, lastSyncTime)
if err != nil {
// This is the legacy event thrown by manage pod loop
// all other events are now dispatched from syncPodFn
p.recorder.Eventf(update.Pod, v1.EventTypeWarning, events.FailedSync, "error determining status: %v", err)
return err
}
err = p.syncPodFn(syncPodOptions{
mirrorPod: update.MirrorPod,
pod: update.Pod,
podStatus: status,
killPodOptions: update.KillPodOptions,
updateType: update.UpdateType,
})
lastSyncTime = time.Now()
return err
}()
// notify the call-back function if the operation succeeded or not
if update.OnCompleteFunc != nil {
update.OnCompleteFunc(err)
}
if err != nil {
// IMPORTANT: we do not log errors here, the syncPodFn is responsible for logging errors
klog.ErrorS(err, "Error syncing pod, skipping", "pod", klog.KObj(update.Pod), "podUID", update.Pod.UID)
}
p.wrapUp(update.Pod.UID, err)
}
}
syncPodFn 是核心处理内容,它的实际实现在 kubelet.go 文件中。我们先来看最后收尾的 wrapUp 函数
pkg/kubelet/pod_workers.go:262
func (p *podWorkers) wrapUp(uid types.UID, syncErr error) {
// Requeue the last update if the last sync returned error.
switch {
case syncErr == nil:
// No error; requeue at the regular resync interval.
p.workQueue.Enqueue(uid, wait.Jitter(p.resyncInterval, workerResyncIntervalJitterFactor))
case strings.Contains(syncErr.Error(), NetworkNotReadyErrorMsg):
// Network is not ready; back off for short period of time and retry as network might be ready soon.
p.workQueue.Enqueue(uid, wait.Jitter(backOffOnTransientErrorPeriod, workerBackOffPeriodJitterFactor))
default:
// Error occurred during the sync; back off and then retry.
p.workQueue.Enqueue(uid, wait.Jitter(p.backOffPeriod, workerBackOffPeriodJitterFactor))
}
p.checkForUpdates(uid)
}
pkg/kubelet/pod_workers.go:278
func (p *podWorkers) checkForUpdates(uid types.UID) {
p.podLock.Lock()
defer p.podLock.Unlock()
if workUpdate, exists := p.lastUndeliveredWorkUpdate[uid]; exists {
p.podUpdates[uid] <- workUpdate
delete(p.lastUndeliveredWorkUpdate, uid)
} else {
p.isWorking[uid] = false
}
}
checkForUpdates 函数负责从 lastUndeliveredWorkUpdate 中取出待处理的消息然后塞到 podUpdates channel 中。如果没有任何消息需要处理,那么会将 isWorking 置为 false,允许外部从 UpdatePod 这条路径传入消息
整个 PodWorker 的工作逻辑如下图