The Prometheus Operator for Kubernetes provides easy monitoring definitions for Kubernetes services and deployment and management of Prometheus instances.
Once installed, the Prometheus Operator provides the following features:
Create/Destroy: Easily launch a Prometheus instance for your Kubernetes namespace, a specific application or team easily using the Operator.
Simple Configuration: Configure the fundamentals of Prometheus like versions, persistence, retention policies, and replicas from a native Kubernetes resource.
Target Services via Labels: Automatically generate monitoring target configurations based on familiar Kubernetes label queries; no need to learn a Prometheus specific configuration language.
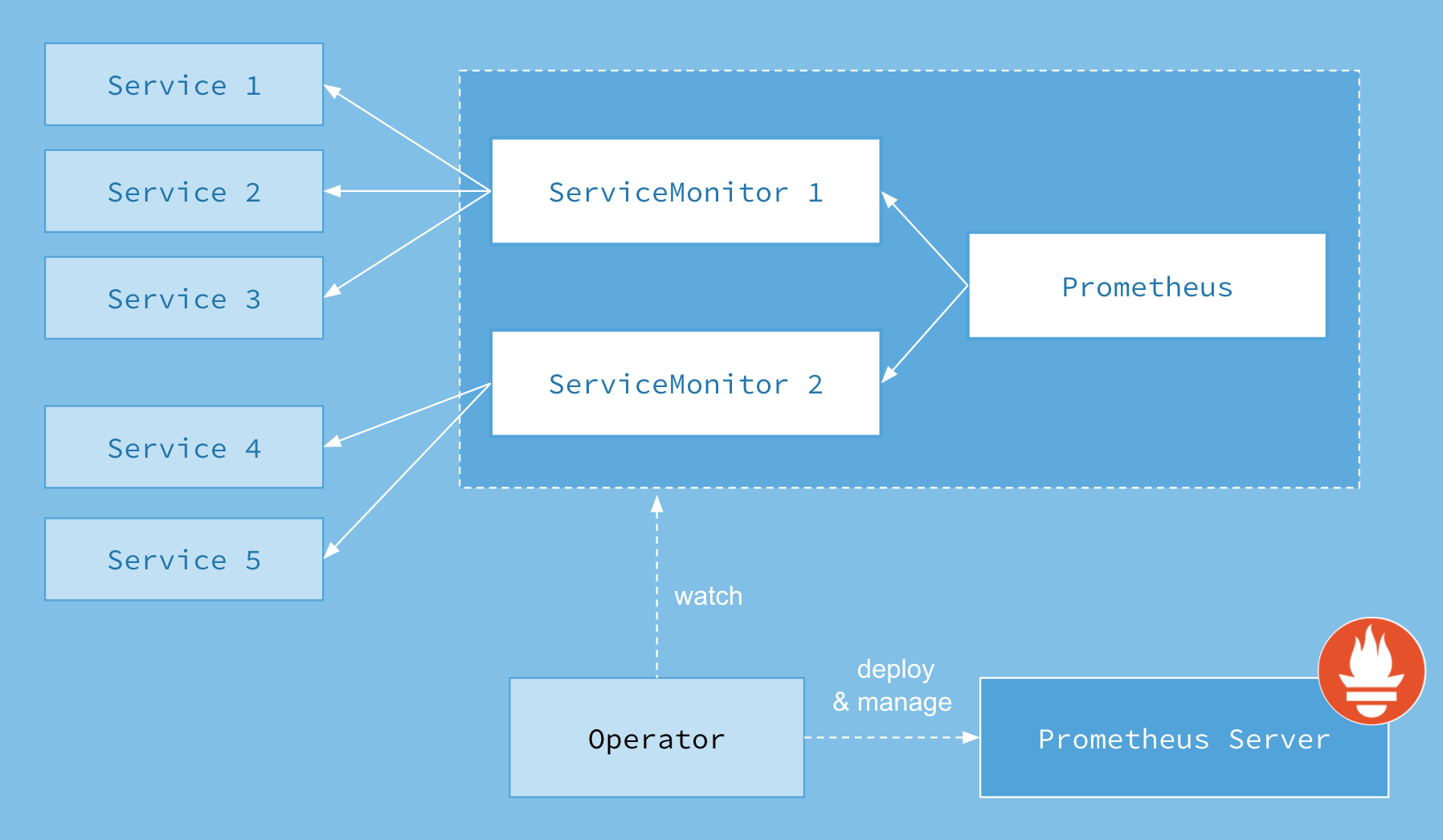
上图并不完整,PR#1333 引入了 RuleFule CRD,现在已经改名为 PrometheusRules。简单来说,Prometheus Operator 将 Prometheus 原生的配置抽象成了 Kubernetes 中的资源。通过资源的定义,Operator 会自动去更新 Prometheus 的配置然后 reload
我们下面来分析一下 Prometheus Operator 具体的架构
Install#
安装参考:
git clone https://github.com/coreos/prometheus-operator.git
cd prometheus/operator/contrib/kube-prometheus
kubectl apply -f manifests/
nohup kubectl --namespace monitoring port-forward svc/prometheus-k8s 9090 &
# visit localhost:9090
Under the hood#
Operator 的启动代码在 cmd/operator/main.go
func Main() int {
// ... 根据参数创建 logger
po, _ := prometheuscontroller.New(cfg, log.With(logger, "component", "prometheusoperator"))
ao, _ := alertmanagercontroller.New(cfg, log.With(logger, "component", "alertmanageroperator"))
mux := http.NewServeMux()
web, _ := api.New(cfg, log.With(logger, "component", "api"))
web.Register(mux)
l, _ := net.Listen("tcp", ":8080")
// 注册&提供自身 metrics
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
wg, ctx := errgroup.WithContext(ctx)
wg.Go(func() error { return po.Run(ctx.Done()) })
wg.Go(func() error { return ao.Run(ctx.Done()) })
srv := &http.Server{Handler: mux}
go srv.Serve(l)
term := make(chan os.Signal)
signal.Notify(term, os.Interrupt, syscall.SIGTERM)
select {
case <-term:
logger.Log("msg", "Received SIGTERM, exiting gracefully...")
case <-ctx.Done():
}
cancel()
if err := wg.Wait(); err != nil {
logger.Log("msg", "Unhandled error received. Exiting...", "err", err)
return 1
}
return 0
}
可以看到,它主要做了四件事情
- main goroutine 初始化并管理其他 goroutine
- http server 监听 8080,提供自身的 metrics
- prometheus controller,管理 Prometheus
- alertmanager controller,管理 AlertManager
再来看 prometheuscontroller 的初始化与运行
// pkg/prometheus/operator.go
func New(conf Config, logger log.Logger) (*Operator, error) {
cfg, _ := k8sutil.NewClusterConfig(conf.Host, conf.TLSInsecure, &conf.TLSConfig)
client, _ := kubernetes.NewForConfig(cfg)
crdclient, _ := apiextensionsclient.NewForConfig(cfg)
mclient, _ := monitoringclient.NewForConfig(cfg)
// ... 若启动时传入的 `kubelet-service` 参数,则 `kubeletSyncEnabled` 置为 true,并
// ... 根据参数的值对 `kubeletObjectName`, `kubeletObjectNamespace` 赋值
// ... 若启动时未传入则 `kubeletObjectName`, `kubeletObjectNamespace` 为空字符串,
// ... `kubeletSyncEnabled` 置为 false
c := &Operator{
kclient: client,
mclient: mclient,
crdclient: crdclient,
logger: logger,
queue: workqueue.NewNamedRateLimitingQueue(workqueue.DefaultControllerRateLimiter(), "prometheus"),
host: cfg.Host,
kubeletObjectName: kubeletObjectName,
kubeletObjectNamespace: kubeletObjectNamespace,
kubeletSyncEnabled: kubeletSyncEnabled,
config: conf,
configGenerator: NewConfigGenerator(logger),
}
c.promInf = cache.NewSharedIndexInformer(
listwatch.MultiNamespaceListerWatcher(c.config.Namespaces, func(namespace string) cache.ListerWatcher {
return &cache.ListWatch{
ListFunc: func(options metav1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
return mclient.MonitoringV1().Prometheuses(namespace).List(options)
},
WatchFunc: mclient.MonitoringV1().Prometheuses(namespace).Watch,
}
}),
&monitoringv1.Prometheus{}, resyncPeriod, cache.Indexers{cache.NamespaceIndex: cache.MetaNamespaceIndexFunc},
)
// ... 同样 Watch 了
// ... c.smonInf ServiceMonitors
// ... c.ruleInf PrometheusRules
// ... c.cmapInf ConfigMaps
// ... c.secrInf Secrets
// ... c.ssetInf StatefulSets
// nsResyncPeriod is used to control how often the namespace informer
// should resync. If the unprivileged ListerWatcher is used, then the
// informer must resync more often because it cannot watch for
// namespace changes.
nsResyncPeriod := 15 * time.Second
// If the only namespace is v1.NamespaceAll, then the client must be
// privileged and a regular cache.ListWatch will be used. In this case
// watching works and we do not need to resync so frequently.
if listwatch.IsAllNamespaces(c.config.Namespaces) {
nsResyncPeriod = resyncPeriod
}
c.nsInf = cache.NewSharedIndexInformer(
listwatch.NewUnprivilegedNamespaceListWatchFromClient(c.kclient.Core().RESTClient(), c.config.Namespaces, fields.Everything()),
&v1.Namespace{}, nsResyncPeriod, cache.Indexers{},
)
return c, nil
}
func (c *Operator) Run(stopc <-chan struct{}) error {
defer c.queue.ShutDown()
errChan := make(chan error)
go func() {
v, err := c.kclient.Discovery().ServerVersion()
if err != nil {
errChan <- errors.Wrap(err, "communicating with server failed")
return
}
level.Info(c.logger).Log("msg", "connection established", "cluster-version", v)
if c.config.ManageCRDs {
// 创建 Prometheus, ServiceMonitor, PrometheusRule 三种 CRD,并且等待创建完成
// 若已经存在,则使用已经存在的 CRD 的 ResourceVersion 覆盖更新
if err := c.createCRDs(); err != nil {
errChan <- errors.Wrap(err, "creating CRDs failed")
return
}
}
errChan <- nil
}()
select {
case err := <-errChan:
if err != nil {
return err
}
level.Info(c.logger).Log("msg", "CRD API endpoints ready")
case <-stopc:
return nil
}
go c.worker()
go c.promInf.Run(stopc)
go c.smonInf.Run(stopc)
go c.ruleInf.Run(stopc)
go c.cmapInf.Run(stopc)
go c.secrInf.Run(stopc)
go c.ssetInf.Run(stopc)
go c.nsInf.Run(stopc)
if err := c.waitForCacheSync(stopc); err != nil {
return err
}
c.addHandlers()
if c.kubeletSyncEnabled {
go c.reconcileNodeEndpoints(stopc)
}
<-stopc
return nil
}
这里对于 Prometheus, ServiceMonitors, PrometheusRules, ConfigMaps, Secrets, StatefulSets 几种资源进行了 Watch,然后通过 addHandlers 注册了事件的回调函数
// pkg/prometheus/operator.go
func (c *Operator) addHandlers() {
c.promInf.AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: c.handlePrometheusAdd,
DeleteFunc: c.handlePrometheusDelete,
UpdateFunc: c.handlePrometheusUpdate,
})
// ... c.smonInf.AddEventHandler(
// ... c.ruleInf.AddEventHandler(
// ... c.cmapInf.AddEventHandler(
// ... c.secrInf.AddEventHandler(
// ... c.ssetInf.AddEventHandler(
}
这里以 handlePrometheusAdd 为例
func (c *Operator) handlePrometheusAdd(obj interface{}) {
key, ok := c.keyFunc(obj) // checks for DeletedFinalStateUnknown objects before calling MetaNamespaceKeyFunc.
if !ok {
return
}
level.Debug(c.logger).Log("msg", "Prometheus added", "key", key)
c.triggerByCounter.WithLabelValues(monitoringv1.PrometheusesKind, "add").Inc()
c.enqueue(key)
}
// handlePrometheusUpdate 中比对了新旧资源的 ResourceVersion,只有在不同的情况下才入队
triggerByCounter 记录了事件发生的次数,会以 metrics 的形式暴露出来
# HELP prometheus_operator_triggered_total Number of times a Kubernetes object add, delete or update event triggered the Prometheus Operator to reconcile an object
# TYPE prometheus_operator_triggered_total counter
prometheus_operator_triggered_total{action="add",controller="prometheus",triggered_by="ConfigMap"} 18
prometheus_operator_triggered_total{action="add",controller="prometheus",triggered_by="Prometheus"} 1
prometheus_operator_triggered_total{action="update",controller="prometheus",triggered_by="StatefulSet"} 7
所有的对象会被转化为 key 入队
func (c *Operator) enqueue(obj interface{}) {
if obj == nil {
return
}
key, ok := obj.(string)
if !ok {
key, ok = c.keyFunc(obj)
if !ok {
return
}
}
c.queue.Add(key)
}
worker 将 queue 中的元素出队并且处理。同时也保证了 syncHandler 不会被并发的调用
func (c *Operator) worker() {
for c.processNextWorkItem() {
}
}
func (c *Operator) processNextWorkItem() bool {
key, quit := c.queue.Get()
if quit {
return false
}
defer c.queue.Done(key)
err := c.sync(key.(string)) //
if err == nil {
c.queue.Forget(key)
return true
}
c.reconcileErrorsCounter.With(prometheus.Labels{}).Inc()
// prometheus_operator_reconcile_errors_total{controller="prometheus"} 0
utilruntime.HandleError(errors.Wrap(err, fmt.Sprintf("Sync %q failed", key)))
c.queue.AddRateLimited(key)
return true
}
核心部分位于 sync,它从资源中抽出配置,并且同步,另外还管理 StatefulSet
func (c *Operator) sync(key string) error {
obj, exists, err := c.promInf.GetIndexer().GetByKey(key)
if err != nil {
return err
}
if !exists {
// Dependent resources are cleaned up by K8s via OwnerReferences
return nil
}
p := obj.(*monitoringv1.Prometheus)
p = p.DeepCopy()
p.APIVersion = monitoringv1.SchemeGroupVersion.String()
p.Kind = monitoringv1.PrometheusesKind
if p.Spec.Paused {
return nil
}
level.Info(c.logger).Log("msg", "sync prometheus", "key", key)
// 1) 根据 p 的 `ruleNamespaceSelector` 选择 namespace,
// 如果 `RuleNamespaceSelector` 为空,则默认为 p 所在的 namespace
// 2) 根据 p 的 `ruleSelector` 在指定的 namespace 下获取所有的 PrometheusRule
// 类型的对象,然后根据其 spec 节中的内容获得新的 Rules
// 3) 与当前的 Rules 进行对比,如果未改变则什么都不做
// 若当前没有 ConfigMap 则直接创建新的
// 若改变则删除现在的 ConfigMap,然后根据新的 Rules 创建新的 ConfigMap
// 4) 返回最新的所有的 ConfigMap 名字
// 之后会被 format 到 Prometheus.yaml 中
// rule_files:
// - /etc/prometheus/rules/{configmap-name}/*.yaml
ruleConfigMapNames, err := c.createOrUpdateRuleConfigMaps(p)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// If no service monitor selectors are configured, the user wants to
// manage configuration themselves.
if p.Spec.ServiceMonitorSelector != nil {
// We just always regenerate the configuration to be safe.
// 1) 根据 p 的 `ServiceMonitorNamespaceSelector` 选择 namespace,
// 如果 `ServiceMonitorNamespaceSelector` 为空,则默认为 p 所在的 namespace
// 2) 根据 p 的 `ServiceMonitorSelector` 在指定的 namespace 下获取所有的 ServiceMonitor
// 3) 从 ServiceMonitor 中取 Endpoints,从 p 所在 namespace 中的 Secret 中取
// additional scrape config, additional alert relabel config 等配置
// 然后生成一分新的 Prometheus 的配置,具体逻辑参考 pkg/prometheus/promcfg.go#L102
// 4) 比对现有的 Secret(Prometheus 的配置文件是以 Secret 的形式挂载),然后存在变化就更新
if err := c.createOrUpdateConfigurationSecret(p, ruleConfigMapNames); err != nil {
return errors.Wrap(err, "creating config failed")
}
}
// Create empty Secret if it doesn't exist. See comment above.
s, err := makeEmptyConfigurationSecret(p, c.config)
if err != nil {
return errors.Wrap(err, "generating empty config secret failed")
}
sClient := c.kclient.CoreV1().Secrets(p.Namespace)
// 从 p 的 namespace 获取 secret,如果不存在则创建一个空的
_, err = sClient.Get(s.Name, metav1.GetOptions{})
if apierrors.IsNotFound(err) {
if _, err := c.kclient.Core().Secrets(p.Namespace).Create(s); err != nil && !apierrors.IsAlreadyExists(err) {
return errors.Wrap(err, "creating empty config file failed")
}
}
if !apierrors.IsNotFound(err) && err != nil {
return err
}
// 接下来的代码在创建管理 StatefulSet 及其关联的 Service
// Create governing service if it doesn't exist.
svcClient := c.kclient.Core().Services(p.Namespace)
if err := k8sutil.CreateOrUpdateService(svcClient, makeStatefulSetService(p, c.config)); err != nil {
return errors.Wrap(err, "synchronizing governing service failed")
}
ssetClient := c.kclient.AppsV1beta2().StatefulSets(p.Namespace)
// Ensure we have a StatefulSet running Prometheus deployed.
obj, exists, err = c.ssetInf.GetIndexer().GetByKey(prometheusKeyToStatefulSetKey(key))
if err != nil {
return errors.Wrap(err, "retrieving statefulset failed")
}
newSSetInputHash, err := createSSetInputHash(*p, c.config, ruleConfigMapNames)
if err != nil {
return err
}
sset, err := makeStatefulSet(*p, &c.config, ruleConfigMapNames, newSSetInputHash)
if err != nil {
return errors.Wrap(err, "making statefulset failed")
}
if !exists {
level.Debug(c.logger).Log("msg", "no current Prometheus statefulset found")
level.Debug(c.logger).Log("msg", "creating Prometheus statefulset")
if _, err := ssetClient.Create(sset); err != nil {
return errors.Wrap(err, "creating statefulset failed")
}
return nil
}
oldSSetInputHash := obj.(*appsv1.StatefulSet).ObjectMeta.Annotations[sSetInputHashName]
if newSSetInputHash == oldSSetInputHash {
level.Debug(c.logger).Log("msg", "new statefulset generation inputs match current, skipping any actions")
return nil
}
level.Debug(c.logger).Log("msg", "updating current Prometheus statefulset")
_, err = ssetClient.Update(sset)
sErr, ok := err.(*apierrors.StatusError)
if ok && sErr.ErrStatus.Code == 422 && sErr.ErrStatus.Reason == metav1.StatusReasonInvalid {
level.Debug(c.logger).Log("msg", "resolving illegal update of Prometheus StatefulSet")
propagationPolicy := metav1.DeletePropagationForeground
if err := ssetClient.Delete(sset.GetName(), &metav1.DeleteOptions{PropagationPolicy: &propagationPolicy}); err != nil {
return errors.Wrap(err, "failed to delete StatefulSet to avoid forbidden action")
}
return nil
}
if err != nil {
return errors.Wrap(err, "updating StatefulSet failed")
}
return nil
}
StatefulSet 的生成逻辑在 pkg/prometheus/statefulset.go中,会创建包含三个 Container 的 Pod,分别是 prometheus, prometheus-config-reloader, rules-configmap-reloader
spec:
containers:
- args:
- --web.console.templates=/etc/prometheus/consoles
- --web.console.libraries=/etc/prometheus/console_libraries
- --config.file=/etc/prometheus/config_out/prometheus.env.yaml
- --storage.tsdb.path=/prometheus
- --storage.tsdb.retention=24h
- --web.enable-lifecycle
- --storage.tsdb.no-lockfile
- --web.route-prefix=/
image: quay.io/prometheus/prometheus:v2.5.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: prometheus
ports:
- containerPort: 9090
name: web
protocol: TCP
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/prometheus/config_out
name: config-out
readOnly: true
- mountPath: /prometheus
name: prometheus-k8s-db
- mountPath: /etc/prometheus/rules/prometheus-k8s-rulefiles-0
name: prometheus-k8s-rulefiles-0
- args:
- --log-format=logfmt
- --reload-url=http://localhost:9090/-/reload
- --config-file=/etc/prometheus/config/prometheus.yaml
- --config-envsubst-file=/etc/prometheus/config_out/prometheus.env.yaml
command:
- /bin/prometheus-config-reloader
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: metadata.name
image: quay.io/coreos/prometheus-config-reloader:v0.26.0
name: prometheus-config-reloader
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/prometheus/config
name: config
- mountPath: /etc/prometheus/config_out
name: config-out
- args:
- --webhook-url=http://localhost:9090/-/reload
- --volume-dir=/etc/prometheus/rules/prometheus-k8s-rulefiles-0
image: quay.io/coreos/configmap-reload:v0.0.1
name: rules-configmap-reloader
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/prometheus/rules/prometheus-k8s-rulefiles-0
name: prometheus-k8s-rulefiles-0
volumes:
- name: config
secret:
defaultMode: 420
secretName: prometheus-k8s
- emptyDir: {}
name: config-out
- configMap:
defaultMode: 420
name: prometheus-k8s-rulefiles-0
name: prometheus-k8s-rulefiles-0
- emptyDir: {}
name: prometheus-k8s-db
prometheus就是我们的prometheus实例prometheus-config-reloader的代码在cmd/prometheus-config-reloader/main.go,其实借助了"github.com/improbable-eng/thanos/pkg/reloader"来 watch/etc/prometheus/config/prometheus.yaml,并替换配置里的环境变量生成/etc/prometheus/config_out/prometheus.env.yaml,通过 Prometheus 原生提供的-/reload接口来更新配置。注意这里 Prometheus 所使用的配置文件是替换后的prometheus.env.yamlrules-configmap-reloader使用的是https://github.com/jimmidyson/configmap-reload,它 watch 了 Prometheus 的告警规则和记录规则,然后也是通过-/reload去 reload Prometheus
Prometheus 的大致结构如下
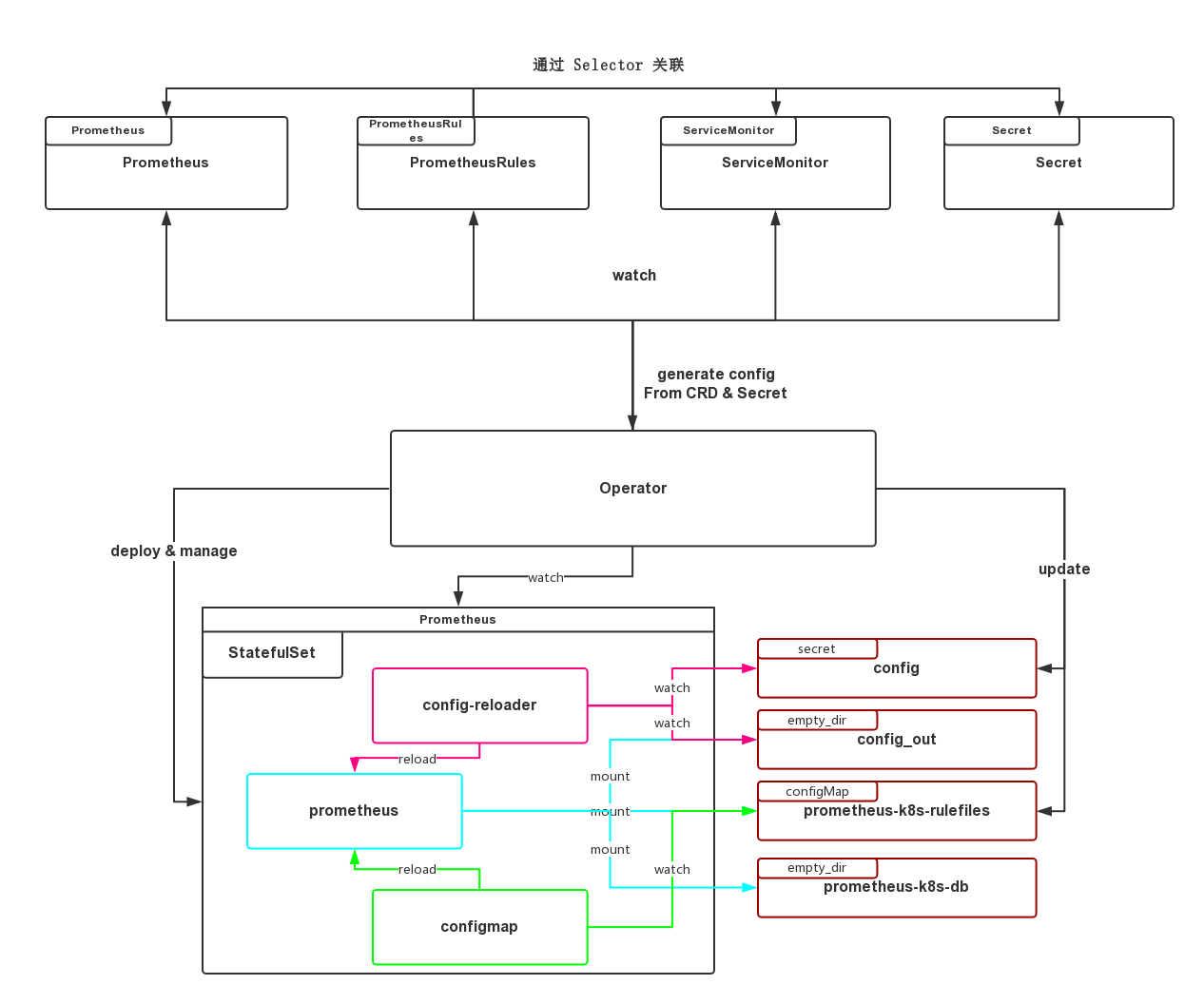
如有错误,欢迎纠正