本文代码取自 Redis 4.0.9,commit sha 为 3150c672442b2275d75a1b6cedf45084019f4d57
我们平常所使用到的 Redis 数据结构 String、Hash、List 等都是 redisObject,就算同一个类型也会有不同的底层数据结构表示,比如
127.0.0.1:6379> SADD simple_set 1 2 3
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT ENCODING simple_set
"intset"
127.0.0.1:6379> SADD simple_set 'string'
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT ENCODING simple_set
"hashtable"
当集合的元素均为整数时且保存的元素数量不超过 512 个时,Set 会使用 intset 作为底层表示,否则便会使用 hashtable
SDS(simple dynamic string) 是 Redis 内部所使用的字符串类型,用于整个 k/v 空间的 k 和 String 类型的底层表示,其定义如下
// sds.h
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {
uint8_t len; /* used */
uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {
uint16_t len; /* used */
uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
// 省略类似的 sdshdr32,sdshdr64 的定义
__attribute__ ((__packed__)) 取消结构体的内存对齐,可以参考 GCC-Type-Attributes
sdshdr8、sdshdr16、sdshdr32、sdshdr64 是针对字符串长度所做的优化,可以减少 len 和 alloc field 所占用的空间。
len 为字符串的真实长度,不包含 \0;alloc 为 buf 的分配长度,同样不包含 \0
flags 的低三位存储了类型 #define SDS_TYPE_8 1; #define SDS_TYPE_16 2
char buf[] 是 C99 下的 Zero Length Array
下面来看字符串的创建
// sds.c
/* Create a new sds string starting from a null terminated C string. */
sds sdsnew(const char *init) {
size_t initlen = (init == NULL) ? 0 : strlen(init);
return sdsnewlen(init, initlen);
}
核心部分位于 sdsnewlen 中
// sds.c
sds sdsnewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen) { // sds 类型即 char *,定义于 sds.h
void *sh;
sds s;
char type = sdsReqType(initlen); // 内联函数,根据字符串长度来选择合适的 SDS 表示
/* Empty strings are usually created in order to append. Use type 8
* since type 5 is not good at this. */
if (type == SDS_TYPE_5 && initlen == 0) type = SDS_TYPE_8;
int hdrlen = sdsHdrSize(type); // 计算 SDS 结构体大小
unsigned char *fp; /* flags pointer. */
sh = s_malloc(hdrlen+initlen+1); // 需要包含 \0
if (!init)
memset(sh, 0, hdrlen+initlen+1);
if (sh == NULL) return NULL;
s = (char*)sh+hdrlen; // 计算 buf 的起始地址
fp = ((unsigned char*)s)-1; // flag
switch(type) {
case SDS_TYPE_8: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(8,s); // [1]
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = initlen;
*fp = type;
break;
}
case SDS_TYPE_16: {
SDS_HDR_VAR(16,s);
sh->len = initlen;
sh->alloc = initlen;
*fp = type;
break;
}
// 省略 SDS_TYPE_32 和 SDS_TYPE_64
}
if (initlen && init)
memcpy(s, init, initlen); // 拷贝字符串至 buf
s[initlen] = '\0';
return s; // 注意这里返回的是 s,而不是 sh
}
[1] 处 SDS_HDR_VAR 是一个宏
// sds.h
#define SDS_HDR_VAR(T,s) struct sdshdr##T *sh = (void*)((s)-(sizeof(struct sdshdr##T)));
## 为宏定义中的连接符,在上例中便会被替换为
struct sdshdr8 *sh = (void*)((s)-(sizeof(struct sdshdr8)));
将 sh 指向结构体的起始地址
下面再来看一下字符串的拼接操作 sdscat 和 sdscatsds
// sds.c
/* Append the specified null termianted C string to the sds string 's'.
*
* After the call, the passed sds string is no longer valid and all the
* references must be substituted with the new pointer returned by the call. */
sds sdscat(sds s, const char *t) {
return sdscatlen(s, t, strlen(t));
}
/* Append the specified sds 't' to the existing sds 's'.
*
* After the call, the modified sds string is no longer valid and all the
* references must be substituted with the new pointer returned by the call. */
sds sdscatsds(sds s, const sds t) {
return sdscatlen(s, t, sdslen(t));
}
sdscatlen 的实现如下
sds sdscatlen(sds s, const void *t, size_t len) {
size_t curlen = sdslen(s);
s = sdsMakeRoomFor(s,len);
if (s == NULL) return NULL;
memcpy(s+curlen, t, len); // 拼接
sdssetlen(s, curlen+len); // 重设 len
s[curlen+len] = '\0';
return s;
}
sdslen 用于计算 SDS 的已用使用长度
// sds.h
#define SDS_TYPE_8 1
#define SDS_TYPE_16 2
#define SDS_TYPE_MASK 7
static inline size_t sdslen(const sds s) {
unsigned char flags = s[-1];
switch(flags&SDS_TYPE_MASK) {
case SDS_TYPE_8:
return SDS_HDR(8,s)->len;
case SDS_TYPE_16:
return SDS_HDR(16,s)->len;
// 有省略
}
return 0;
}
注意 s 为 buf 的起始地址,又因为取消了内存对齐,所以可以通过 s[-1] 来直接定位当前结构体的 flag
在创建 SDS 时,我们 buf 的长度就是字符串长度+1。如果直接将追加到 buf 中,那么显然会造成缓冲区溢出,所以这里需要通过 sdsMakeRoomFor 进行扩容
// sds.c
sds sdsMakeRoomFor(sds s, size_t addlen) {
void *sh, *newsh;
size_t avail = sdsavail(s); // 内联函数,返回 alloc-len
size_t len, newlen;
char type, oldtype = s[-1] & SDS_TYPE_MASK;
int hdrlen;
/* Return ASAP if there is enough space left. */
if (avail >= addlen) return s; // 空间充足
len = sdslen(s);
sh = (char*)s-sdsHdrSize(oldtype);
newlen = (len+addlen);
if (newlen < SDS_MAX_PREALLOC) // 1024*1024 即 1M
newlen *= 2;
else
newlen += SDS_MAX_PREALLOC;
type = sdsReqType(newlen); // 根据连接后字符串长度计算新的类型
/* Don't use type 5: the user is appending to the string and type 5 is
* not able to remember empty space, so sdsMakeRoomFor() must be called
* at every appending operation. */
if (type == SDS_TYPE_5) type = SDS_TYPE_8;
hdrlen = sdsHdrSize(type);
if (oldtype==type) {
newsh = s_realloc(sh, hdrlen+newlen+1);
if (newsh == NULL) return NULL;
s = (char*)newsh+hdrlen;
} else {
/* Since the header size changes, need to move the string forward,
* and can't use realloc */
newsh = s_malloc(hdrlen+newlen+1);
if (newsh == NULL) return NULL;
memcpy((char*)newsh+hdrlen, s, len+1);
s_free(sh);
s = (char*)newsh+hdrlen;
s[-1] = type;
sdssetlen(s, len); // 因为仅仅是扩容,并未连接字符串,所以 len 还是原来的
}
sdssetalloc(s, newlen); // 更改 alloc Field
return s;
}
SDS 采取了空间预分配策略,不仅会为 SDS 分配修改所必须的空间,还会为 SDS 分配额外的未使用空间
- 如果对 SDS 进行修改之后,SDS 的长度依然小于 1M,那么会分配和新长度同样大小的未使用空间
- 如果对 SDS 进行修改之后,SDS 的长度将大于等于 1M,那么将多分配 1M 的未使用空间
这种优化使得不必每次进行字符串连接都进行 realloc
同样地,对于缩减字符串的操作,我们也应当释放不再使用的空间。不过 SDS 使用的是惰性策略
// sds.c
/* Remove the part of the string from left and from right composed just of
* contiguous characters found in 'cset', that is a null terminted C string.
*
* After the call, the modified sds string is no longer valid and all the
* references must be substituted with the new pointer returned by the call.
*
* Example:
*
* s = sdsnew("AA...AA.a.aa.aHelloWorld :::");
* s = sdstrim(s,"Aa. :");
* printf("%s\n", s);
*
* Output will be just "Hello World".
*/
sds sdstrim(sds s, const char *cset) {
char *start, *end, *sp, *ep;
size_t len;
sp = start = s;
ep = end = s+sdslen(s)-1;
while(sp <= end && strchr(cset, *sp)) sp++;
while(ep > sp && strchr(cset, *ep)) ep--;
len = (sp > ep) ? 0 : ((ep-sp)+1);
if (s != sp) memmove(s, sp, len);
s[len] = '\0';
sdssetlen(s,len);
return s;
}
可见 SDS 并没有立即释放不用的空间,仅仅是修改了 len 的大小和 \0 的位置。SDS 提供了缩小空间的操作 sdsRemoveFreeSpace,但是是否进行由调用方决定。比如调整客户端输入缓冲区 querybuf 的大小
// sds.c
sds sdsRemoveFreeSpace(sds s) {
void *sh, *newsh;
char type, oldtype = s[-1] & SDS_TYPE_MASK;
int hdrlen, oldhdrlen = sdsHdrSize(oldtype);
size_t len = sdslen(s);
sh = (char*)s-oldhdrlen;
/* Check what would be the minimum SDS header that is just good enough to
* fit this string. */
type = sdsReqType(len);
hdrlen = sdsHdrSize(type);
/* If the type is the same, or at least a large enough type is still
* required, we just realloc(), letting the allocator to do the copy
* only if really needed. Otherwise if the change is huge, we manually
* reallocate the string to use the different header type. */
if (oldtype==type || type > SDS_TYPE_8) {
newsh = s_realloc(sh, oldhdrlen+len+1);
if (newsh == NULL) return NULL;
s = (char*)newsh+oldhdrlen;
} else {
newsh = s_malloc(hdrlen+len+1);
if (newsh == NULL) return NULL;
memcpy((char*)newsh+hdrlen, s, len+1);
s_free(sh);
s = (char*)newsh+hdrlen;
s[-1] = type;
sdssetlen(s, len);
}
sdssetalloc(s, len);
return s;
}
SDS 的内存布局如图
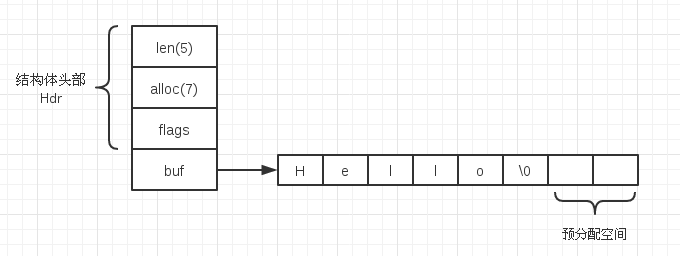
相较 C 字符串,SDS 具有以下的优点
- 常数复杂度获取字符串长度
- 杜绝缓冲区溢出
- 减少修改字符串长度时所需的内存重分配次数
- 二进制安全
- 兼容部分 C 字符串函数