我们总共支持 256 个中断,所以这里创建一个数组
pub static IDT: Mutex<[IdtEntry; 256]> = Mutex::new([IdtEntry::new(); 256]);
接下来初始化并载入 IDT
pub fn init() {
let ptr: DescriptorTablePointer =
DescriptorTablePointer::new_idtp(&IDT.lock()[..]);
unsafe { dtables::lidt(&ptr) };
}
ISR 被调用时我们需要进行 pushad 和 popad,所以添加下面几个 macro
#[macro_export]
macro_rules! scratch_push {
() => (asm!(
"push rax
push rcx
push rdx
push rdi
push rsi
push r8
push r9
push r10
push r11"
: : : : "intel", "volatile"
));
}
#[macro_export]
macro_rules! scratch_pop {
() => (asm!(
"pop r11
pop r10
pop r9
pop r8
pop rsi
pop rdi
pop rdx
pop rcx
pop rax"
: : : : "intel", "volatile"
));
}
#[macro_export]
macro_rules! preserved_push {
() => (asm!(
"push rbx
push rbp
push r12
push r13
push r14
push r15"
: : : : "intel", "volatile"
));
}
#[macro_export]
macro_rules! preserved_pop {
() => (asm!(
"pop r15
pop r14
pop r13
pop r12
pop rbp
pop rbx"
: : : : "intel", "volatile"
));
}
#[macro_export]
macro_rules! interrupt {
($name:ident, $body:expr) => {
#[naked]
unsafe extern fn $name() {
#[inline(never)]
fn inner() {
$body
}
scratch_push!();
preserved_push!();
inner();
preserved_pop!();
scratch_pop!();
iret!();
intrinsics::unreachable();
}
};
}
feature #[naked] 可以使函数没有栈帧上的操作,比如
push ebp
mov ebp, esp
...
ret
尝试添加
pub fn init() {
// ...
interrupt!(isr32, {
pic::send_eoi(32);
});
interrupt!(isr33, {
let scancode = unsafe { inb(0x60) };
if let Some(c) = keyboard::from_scancode(scancode as usize) {
kprint!("{}", c);
}
pic::send_eoi(33);
});
// IDT Table
IDT.lock()[32].set_func(isr32);
IDT.lock()[33].set_func(isr33);
unsafe { enable(); }
}
因为我们 PIC 被映射到了 0X20 的位置,所以 IDT 的 32 为 IRQ0(定时器),33 为 IRQ1(键盘),以此类推。当键盘中断发生时可以读取 0x60 来获取扫描码然后转换成按键,这里可以参考 Keyboard Scan Codes
pub fn from_scancode(code: usize) -> Option<char> {
let printable = match code {
0x1e => 'a',
0x30 => 'b',
0x2e => 'c',
// ...
_ => return None,
};
Some(printable)
}
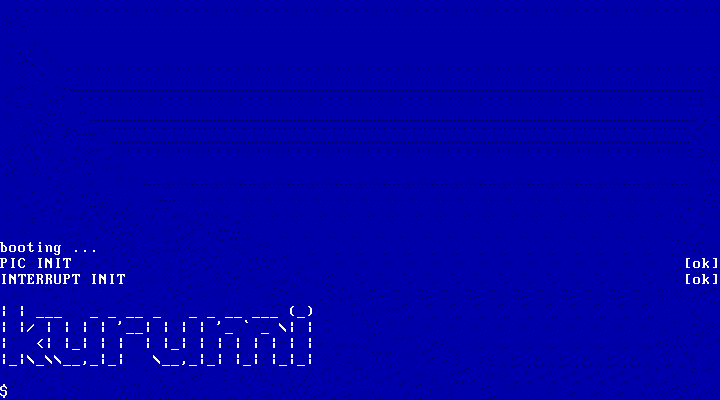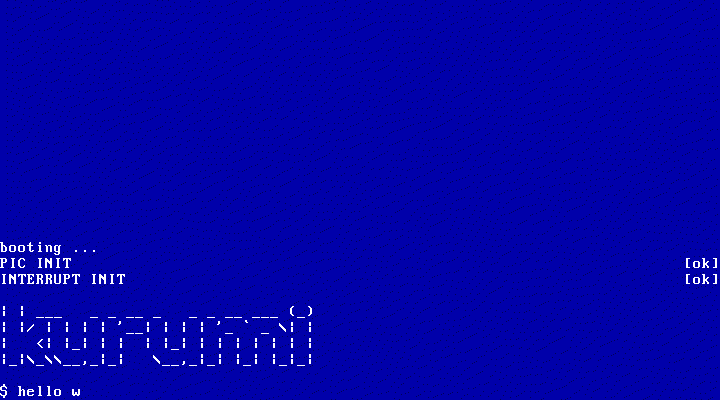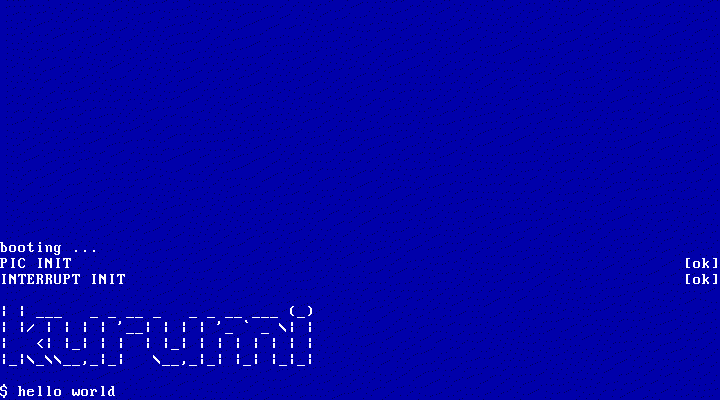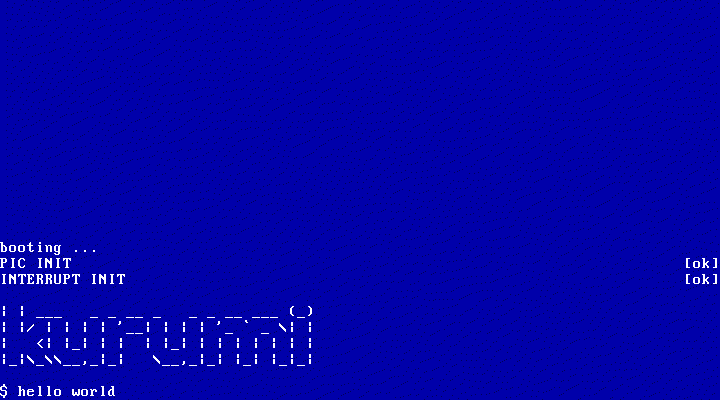
现在我们的 OS 可以输入了