关于 real mode、protected mode、long mode 的模式可以参考 Wiki
进入 long mode 前我们要开启 paging
Basics#
分页(paging)是内存管理的一种手段。在分页内存管理中,把物理地址空间(physical addr)划分为许多个固定大小的帧(frame),把虚拟地址空间(virtual addr)也划分为多个固定大小的页(page),物理地址空间和虚拟地址空间的映射关系存储在页表(page table)中。每个进程都会持有一个页表,进程直接访问的是虚拟地址,由 CPU 中的 MMU 实现虚拟地址到物理地址的转换。分页机制能够让程序可以在逻辑上连续、物理上离散
考虑大小为 64 byte 的物理地址空间,我们将其分为 4 个 frame,每个 frame 大小为 16 byte。我们可以使用 6 bit 来表示全部的物理地址空间,像下面这样划分这 6 个bit
VPN | offset
-------------------------
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
-------------------------
前两位用作虚拟页号(virtual page number,aka VPN),后四位用作每一页的偏移量,4 bit 正好可以表达 16 byte。这样一来当我们想要访问 21 号地址时,将其二进制 010101 按上述原则划分,得到 VPN 为 1,页内偏移量为 5。此时去查找页表中编号为 5 的那一页,然后转换成实际的物理地址加上偏移量便可以得到真正的地址
但是这种简单的分页的页表占用空间比较大。比如x86 4GB 内存,每页大小为 4KB,那么便需要 20 bit 用作 VPN,12 bit 用作偏移量。每一个页表占用 4MB(2^20) 内存空间,并且页表是进程独立的,所以 100 个进程就要 400 MB 的页表
Paging in x86#
x86 通常使用了两级页表,第一级称为页目录表,存储在一个 4KB 的物理页中,页目录表共有 1024 个表项,其中每个表项为 4 byte,页表项中包含对应第二级表所在的基地址。第二级表称为页表,每个页表也安排在一个 4KB 的页中,每张页表中有 1024 个表项,每个表项为 4 byte长,包含对应的物理地址。因为每级只有 1024 个,所以 20 bit 就可以表达,而每一项占用 4 byte,那么便会剩下 12 bit 的空间。这部分空间用作属性位
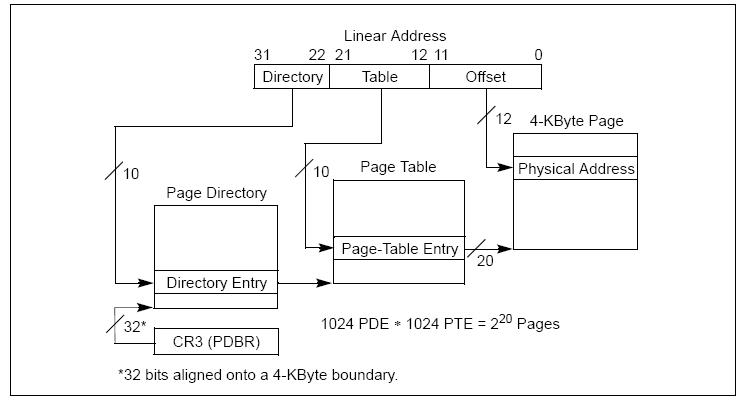
访问时 CPU 首先会把控制寄存器 CR3 的高 20 位 作为页目录表所在的物理基地址,再把待访问地址的高 10 位(即2231位)作为页目录表的索引,查找到对应的页目录表项,这个表项中所包含的高 20 位是对应的页表所在物理页的物理基地址;然后,再把待访问地址的中间 10 位(即1221位)作为页表中的页表项索引,查找到对应的页表项。此表项的高 20 位用作最终物理地址的高 20 位,与待访问地址的低12位进行组合便可以得出最终的物理地址
另外需注意这不是 唯一的 策略,详细可以参考 Protected/compatibility mode (32-bit) page map - OSDev Wiki
Paging in long mode#
在 long mode 下分为 4 个层级
- Page-Map Level-4 Table (PML4)
- Page-Directory Pointer Table (PDP)
- Page-Directory Table (PD)
- Page Table (PT)
每一个页表包含 512 项,每一个项占用 8 字节,所以占用 4096 bytes。就像 x86 二级页表一样,自上而下每一页表指向下一层级的页表
页表项结构如下
| Bit(s) | Name | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | present | the page is currently in memory |
| 1 | writable | it's allowed to write to this page |
| 2 | user accessible | if not set, only kernel mode code can access this page |
| 3 | write through caching | writes go directly to memory |
| 4 | disable cache | no cache is used for this page |
| 5 | accessed | the CPU sets this bit when this page is used |
| 6 | dirty | the CPU sets this bit when a write to this page occurs |
| 7 | huge page/null | must be 0 in P1 and P4, creates a 1GiB page in P3, creates a 2MiB page in P2 |
| 8 | global | page isn't flushed from caches on address space switch (PGE bit of CR4 register must be set) |
| 9-11 | available | can be used freely by the OS |
| 12-51 | physical address | the page aligned 52bit physical address of the frame or the next page table |
| 52-62 | available | can be used freely by the OS |
| 63 | no execute | forbid executing code on this page (the NXE bit in the EFER register must be set) |
这里采取另一种分页方式,物理页大小为 2M,将最初的 1G 物理地址空间分配给内核
; boot.asm
section .bss
align 4096
p4_table:
resb 4096
p3_table:
resb 4096
p2_table:
resb 4096
stack_bottom:
resb 64
stack_top:
将 P4 中的第一项指向 P3,P3 的第一项指向 P2,并且划分 P2 到物理地址的映射
set_up_page_tables:
; map first P4 entry to P3 table
mov eax, p3_table
or eax, 0b11 ; present + writable
mov dword [p4_table], eax
; map first P3 entry to P2 table
mov eax, p2_table
or eax, 0b11 ; present + writable
mov dword [p3_table], eax
; map each P2 entry to a huge 2MiB page
mov ecx, 0 ; counter variable
.map_p2_table:
; map ecx-th P2 entry to a huge page that starts at address 2MiB*ecx
mov eax, 0x200000 ; 2MiB
mul ecx ; start address of ecx-th page
or eax, 0b10000011 ; present + writable + huge
mov [p2_table + ecx * 8], eax ; map ecx-th entry
inc ecx ; increase counter
cmp ecx, 512 ; if counter == 512, the whole P2 table is mapped
jne .map_p2_table ; else map the next entry
ret
需要注意的是 P2 中的表项需要设置 huge 位,因为页的大小为 2MiB
Enable Paging#
开启 paging 并进入 long mode 还需要以下的步骤
- 将 P4 的地址写入 CR3 寄存器
- 开启 PAE(Physical Address Extension)
- 在 EFER 寄存器上设置 long mode 标志位
- 允许 paging
enable_paging:
; load P4 to cr3 register (cpu uses this to access the P4 table)
mov eax, p4_table
mov cr3, eax
; enable PAE-flag in cr4 (Physical Address Extension)
mov eax, cr4 ; Set the A-register to control register 4.
or eax, 1 << 5 ; Set the PAE-bit, which is the 6th bit (bit 5).
mov cr4, eax ; Set control register 4 to the A-register.
; set the long mode bit in the EFER MSR (model specific register)
mov ecx, 0xC0000080 ; Set the C-register to 0xC0000080, which is the EFER MSR.
rdmsr ; Read from the model-specific register.
or eax, 1 << 8 ; Set the LM-bit which is the 9th bit (bit 8).
wrmsr ; Write to the model-specific register.
; enable paging in the cr0 register
mov eax, cr0 ; Set the A-register to control register 0.
or eax, 1 << 31 ; Set the PG-bit, which is the 32nd bit (bit 31).
mov cr0, eax ; Set control register 0 to the A-register.
ret
在我们的 kernel 入口添加上对应的函数调用
section .text
bits 32
start:
mov esp, stack_top
call check_cpuid
call check_long_mode
call set_up_page_tables
call enable_paging
Reference#
Entering Long Mode | Writing an OS in Rust
Setting Up Long Mode - OSDev Wiki
Page Tables - OSDev Wiki
